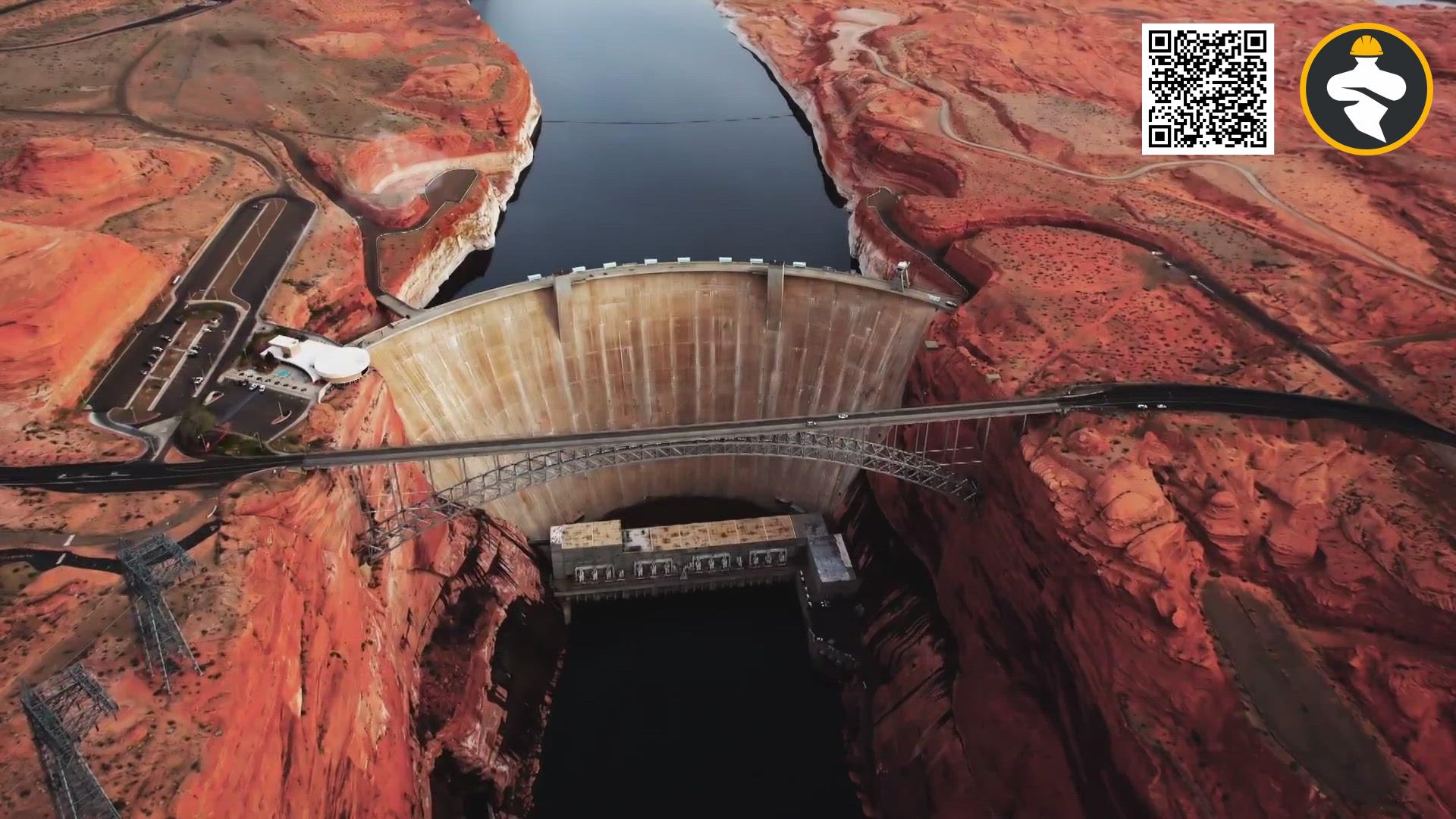
Dams are essential infrastructural elements that support human civilization in numerous ways. They harness the power of water to generate electricity, control floods, and provide irrigation water for agriculture. However, building and maintaining a dam is not an easy task. Dams are subjected to various forces like water pressure, wind, and seismic activity that can cause structural damage and even failure if not designed and constructed properly.
One crucial aspect of dam construction is the quality and durability of the materials used. A dam is only as good as the materials it’s made of. In the past, dams were constructed using conventional materials like concrete, steel, and timber. However, these materials have proved to be inadequate in the face of the extreme forces dams are subjected to.
Fortunately, advances in material science have led to the development of new materials that can withstand these forces and provide superior structural integrity. One such material is high-performance fiber-reinforced cementitious composite (HPFRCC). HPFRCC is a composite material made of cement, fine aggregates, and short, randomly dispersed fibers. The fibers improve the material’s tensile strength and toughness, making it ideal for use in high-stress areas of dams.
Another material that has shown promise in dam construction is geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs). GCLs are composed of a layer of bentonite clay sandwiched between two geotextiles. The bentonite clay swells when it comes into contact with water, creating a watertight barrier that prevents seepage through the dam. GCLs are also more environmentally friendly than traditional liners, as they require less excavation and have a lower carbon footprint.
In addition to material science, sustainability is also an important consideration in dam construction. Dams can have significant environmental impacts, such as altering natural river flows and disrupting aquatic ecosystems. To minimize these impacts, dams must be designed and operated sustainably. This includes incorporating renewable energy sources like hydropower, using efficient irrigation systems to reduce water waste, and implementing measures to mitigate the effects of dam construction on surrounding ecosystems.
In conclusion, building safe and sustainable dams requires a holistic approach that considers not only the design and construction of the dam but also the materials used and the environmental impact of the project. By using advanced materials like HPFRCC and GCLs and implementing sustainable practices, we can ensure that dams continue to provide essential services to our communities while minimizing their negative effects on the environment.
Reference: Globalspec.com