An induction motor is a particular type of alternating current (AC) motor in which the stator windings’ electromagnetic induction produces the electric current needed by the rotor to produce torque. The most common kind of electric motor is used in factories, stores, and homes alike for a variety of purposes, including driving fans, pumps, and conveyor belts. Induction motors are widely used in applications where a constant speed is required due to their reputation for dependability, simplicity of use, and affordability. They are perfect for usage in a variety of applications since they can operate at high rates.
Principles of an induction motor’s operation
An induction motor operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic induction. It has two primary components: a stator, which is the motor’s stationary outer element, and a rotor, which is the motor’s rotating inner component. An induction motor’s stator is normally constructed from a number of windings, or coils, of wire organized in a certain pattern. When an AC is applied to stator windings, a magnetic field is created that spins around the rotor.
The conductors, or bars, that make up the rotor, which is housed inside the stator, are placed in a predetermined configuration. The conductors in the rotor start to flow with current when the stator’s revolving magnetic field passes over it. In turn, this current generates a magnetic field of its own.
The interaction between the rotor’s magnetic field and the stator’s rotating magnetic field results in the production of mechanical energy as the rotor revolves. The frequency of the AC applied to the stator controls how quickly the rotor revolves. High-speed induction motors are noted for their dependability and simplicity.
Various induction motor types
Induction motors come in a variety of designs and are frequently employed in industries, including:
- Induction motors with squirrel cages: These are the induction motors that are most frequently utilized in industrial settings. They are suitable for many industrial applications since they are straightforward, durable, and reliable.
- Slip ring induction motors: These motors are more suited for high beginning torque applications like pumps and fans than squirrel cage motors due to their higher starting torque and power factor.
- Induction motors with double cages: These motors have two sets of squirrel cages, one in each of the rotor and stator. They are appropriate for heavy-duty applications and have a higher starting torque and power factor than squirrel cage motors.
- Induction motors with wound rotors: These motors have a rotor constructed of copper or aluminum wire that has been wound into a cylindrical shape. Compared to squirrel cage motors, they have a higher beginning torque and power factor, but they are also more complicated and require more maintenance.
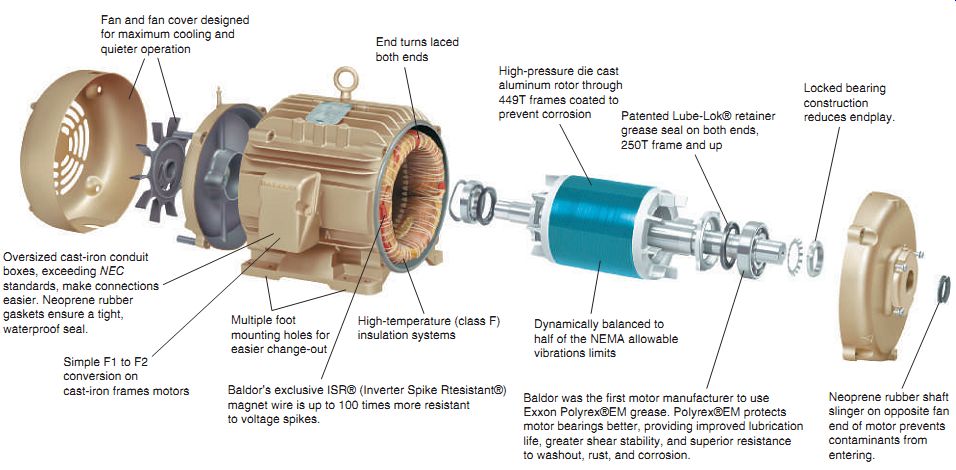
The advantages of induction motors
Induction motors provide a number of benefits over other AC motors, including:
- Due to their simplicity, toughness, and dependability, induction motors are appropriate for a wide range of industrial applications.
- They have a lengthy service life and are simple to maintain.
- Compared to other AC motors like synchronous motors, they are relatively cheap.
These motors are more effective at turning electrical energy into mechanical energy because they have a high power factor. - The three-phase variant is appropriate for applications where a starter is impractical because it is self-starting and does not need an external starter.
- Induction motors are highly suited for a variety of applications thanks to their wide range of speed and power ratings.
- They are perfect for applications requiring precise speed control since they can run at a constant speed.
Induction motor applications
Due to the lack of an initial rotating magnetic field, single-phase induction motors are not self-starting; thus, motor starter circuits are included to start them effectively and securely. A single-phase induction motor is the ideal choice when a small amount of power is needed. In both households and businesses, these motors are used extensively. For instance, they are utilized in drills, pumps, miniature fans, toys, and compressors.
The three-phase induction motors, on the other hand, have the ability to start without the aid of a centrifugal switch, start winding, capacitor, or any other external starting device. Three-phase induction motors are widely used in both residential and business settings due to their inexpensive initial cost, little maintenance needs, and capacity to operate using only the stator as power. They can be used to power lifts, cranes, and lathe equipment, for instance.
Conclusion
Induction motors are a desirable option for commercial and industrial applications due to their long lifespans and cheap total cost of ownership. Applications for these motors include industrial fans, power tools, blowers, pumps, home appliances, machine tools, and disc drives. Due to their lower number of moving parts and minimal maintenance requirements, induction motors are typically more dependable than other kinds of electric motors. They are a cost-effective option for both households and businesses because they are also energy efficient.
Reference: N. Mughees @ globalspec









Excellent blog post. I certainly love this website. Keep it up!