Biotechnology has opened up new possibilities in industrial energy production by designing bacteria that can produce biofuels and other forms of renewable energy. This approach offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to climate change.
The process of designing bacteria for energy production involves genetic engineering, which manipulates the DNA of microorganisms to create new metabolic pathways that enable them to convert organic matter into energy. These pathways can be optimized to produce specific types of biofuels, such as ethanol, butanol, and biodiesel, as well as other forms of energy, such as hydrogen and methane.
One advantage of using bacteria for energy production is their ability to consume a wide range of feedstocks, including waste materials from agriculture, forestry, and food production. This means that they can convert organic waste into energy, reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and reducing greenhouse gas emissions from waste disposal.
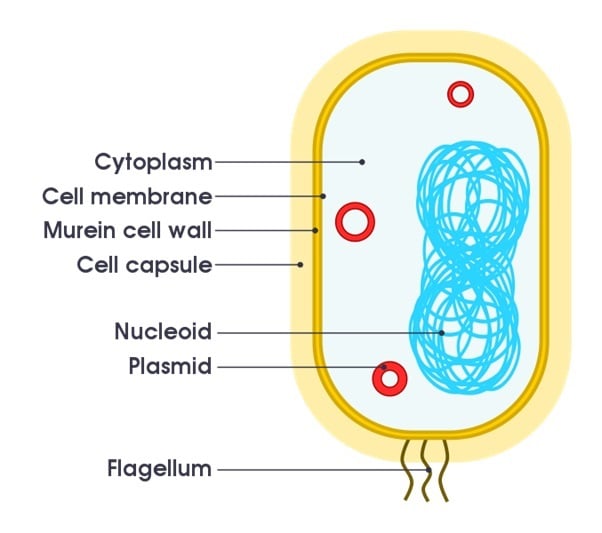
Simple diagram of a bacterium. Source: domdomegg/CC BY-SA 4.0
Another advantage is the scalability of bacterial energy production. Bacteria can be grown in large quantities in bioreactors, which can be easily scaled up or down depending on the demand for energy. This makes bacterial energy production a flexible and adaptable solution to meet the changing needs of industries and communities.
However, there are still challenges to overcome in designing bacteria for industrial energy production. One challenge is the need to optimize the metabolic pathways of bacteria to increase their efficiency and yield. This requires a deep understanding of the biochemical processes involved in energy production and the ability to manipulate them at the genetic level.
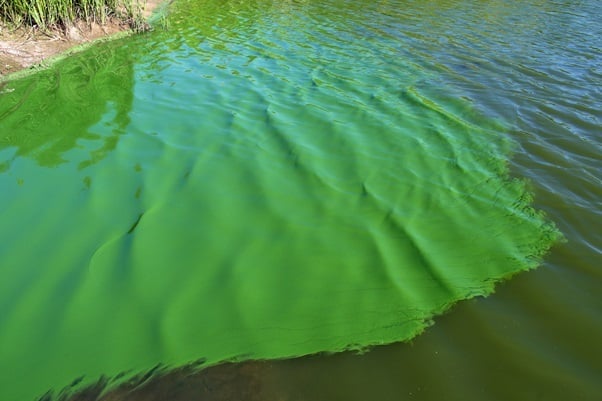

Bloom of cyanobacteria in a freshwater pond. Source: Christian Fischer/CC BY-SA 3.0
Another challenge is the need to ensure the safety and environmental impact of bacterial energy production. There is a risk that genetically modified bacteria could escape from bioreactors and contaminate natural ecosystems, potentially causing harm to human health and the environment. Therefore, it is important to develop robust containment measures and monitoring systems to prevent such incidents.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of bacterial energy production are significant. It offers a sustainable and renewable source of energy that can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the impacts of climate change. As biotechnology continues to advance, designing bacteria for industrial energy production is likely to become an increasingly important frontier in the field.
Reference: GlobalSpec